ENDOSCOPIC ENDONASAL SKULL BASE SURGERY FOR PITUITARY LESIONS: AN AI-ASSISTED CREATIVE WORKFLOW TO DEVELOP AN ANIMATED EDUCATIONAL RESOURCE FOR PATIENTS AND PHYSICIANS
Abstract
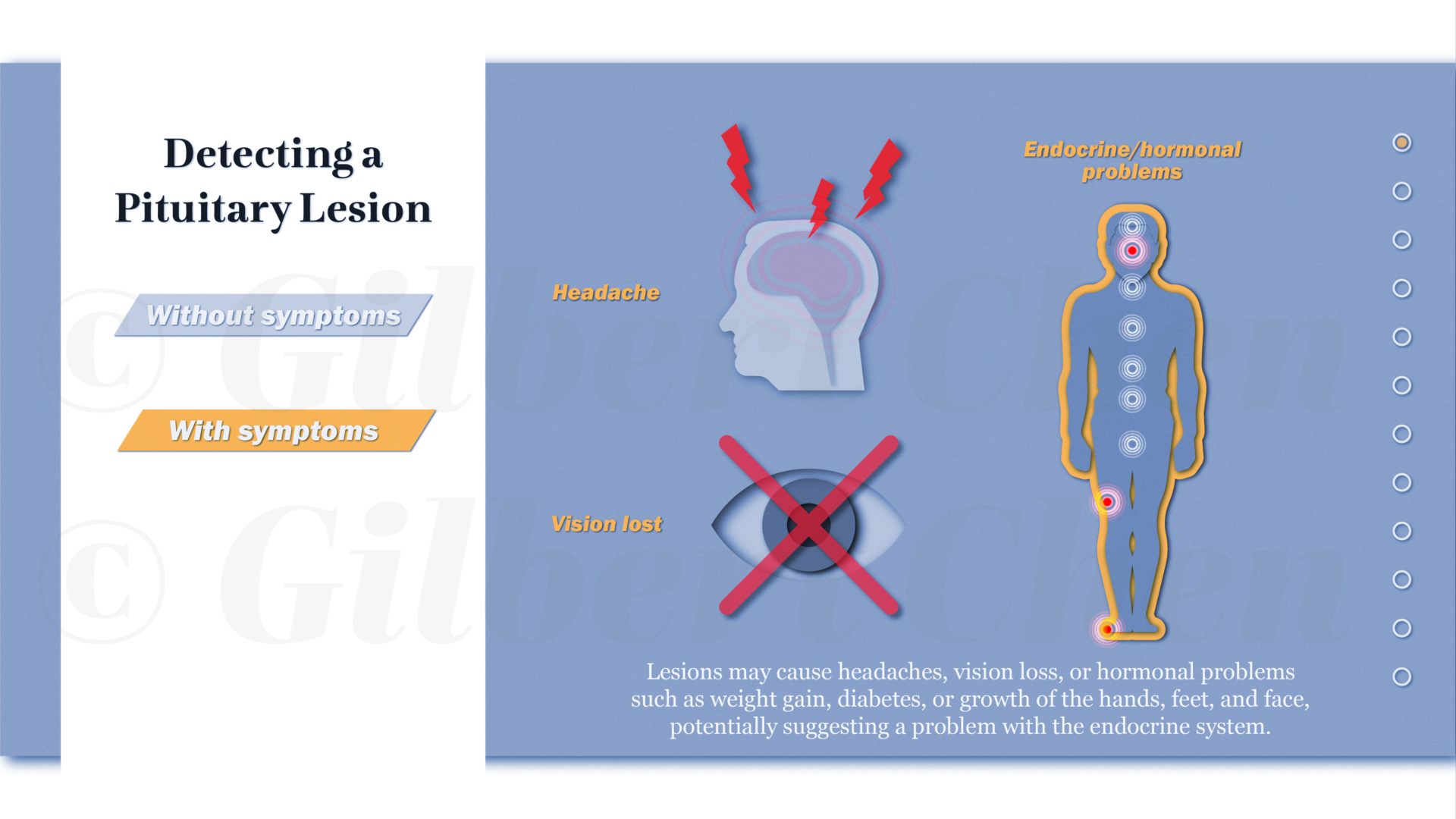
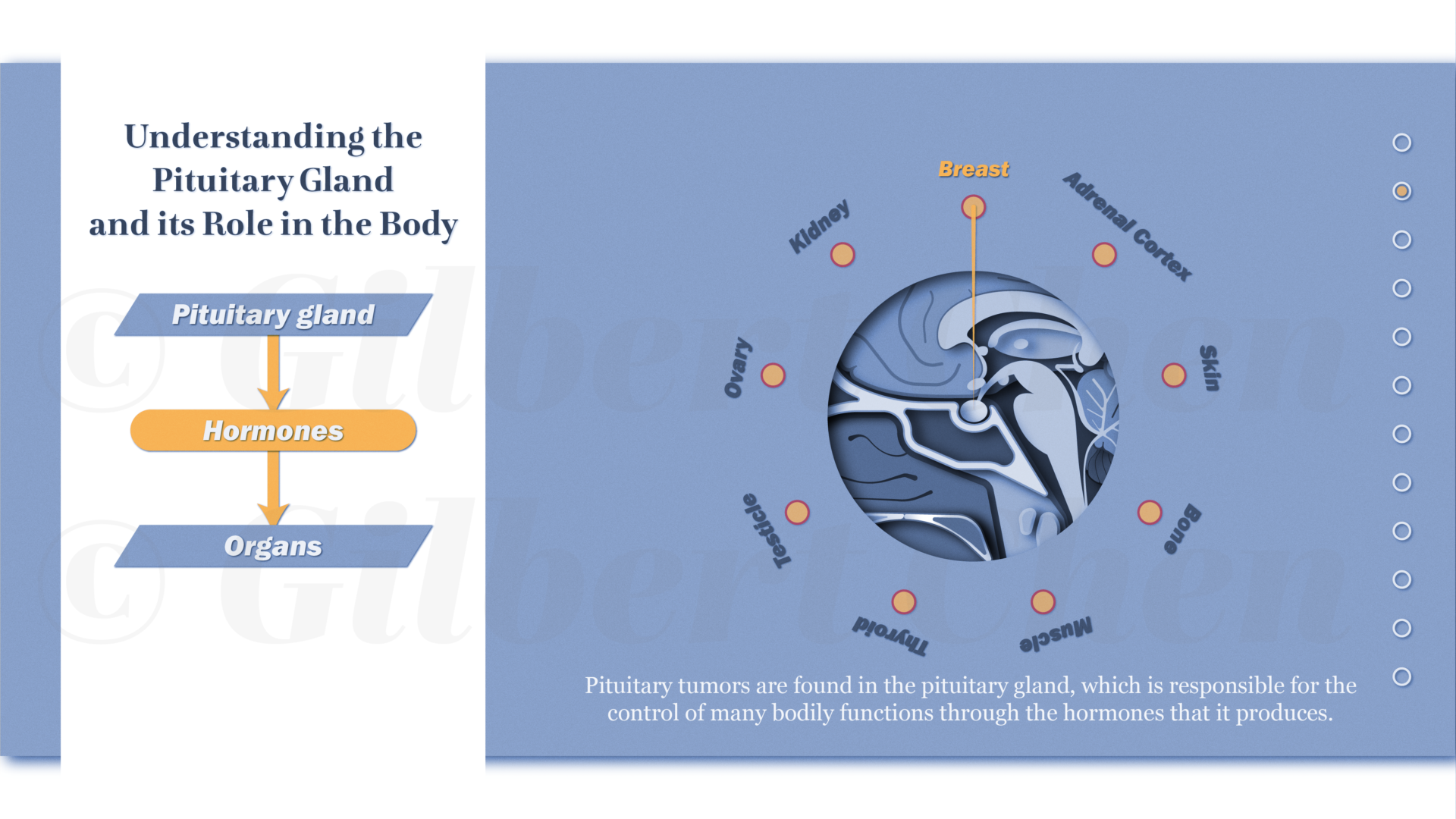
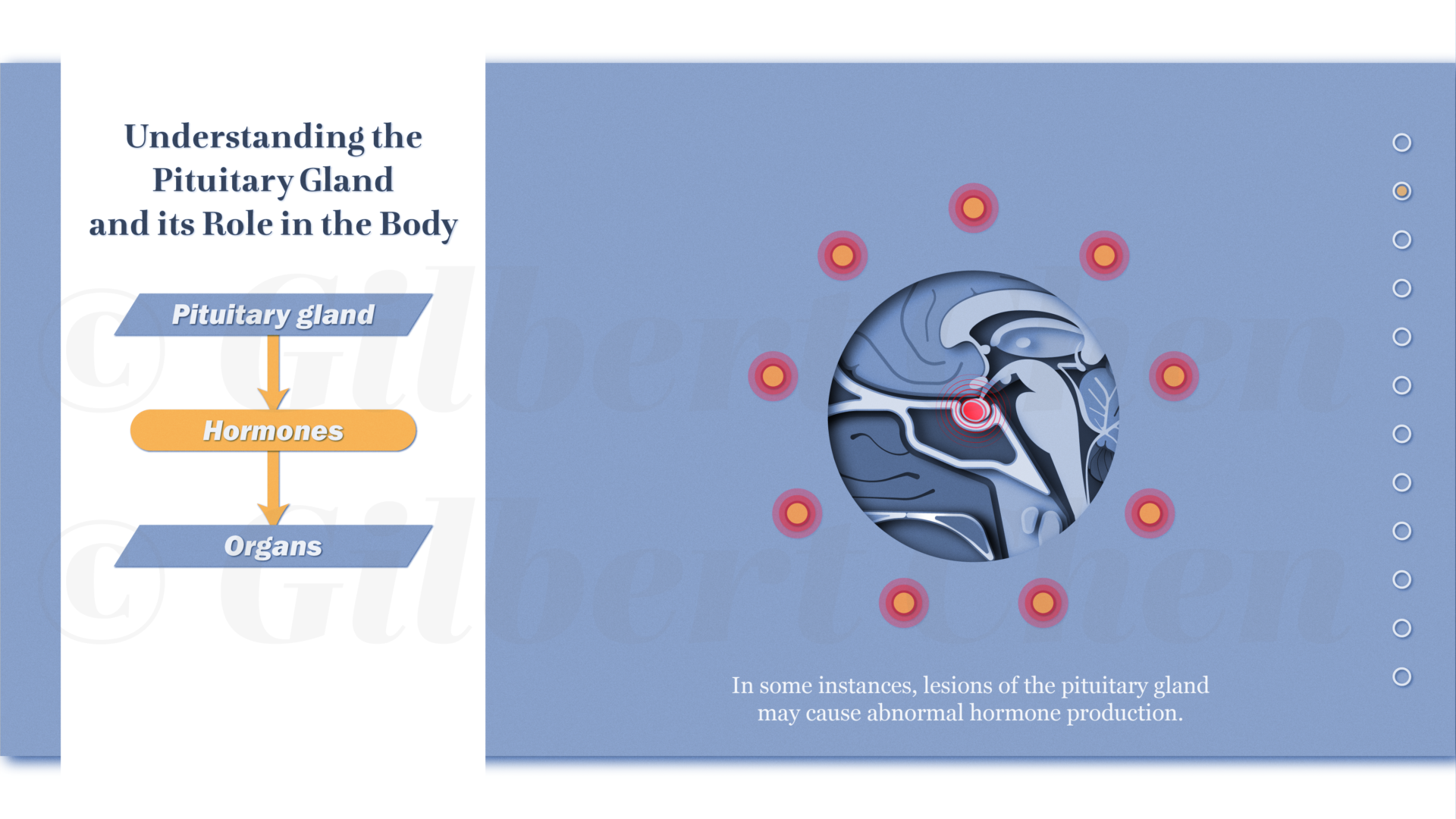
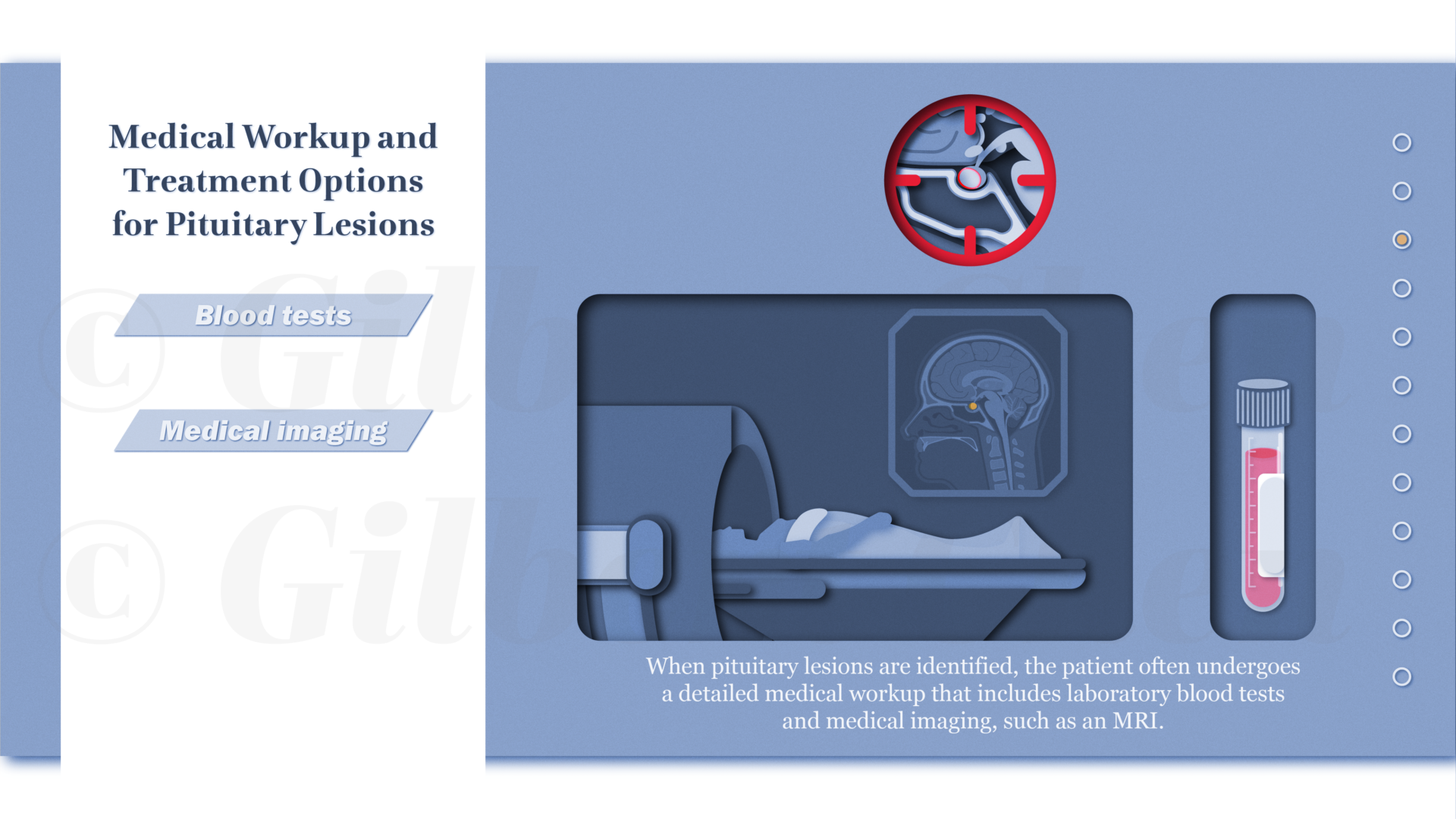
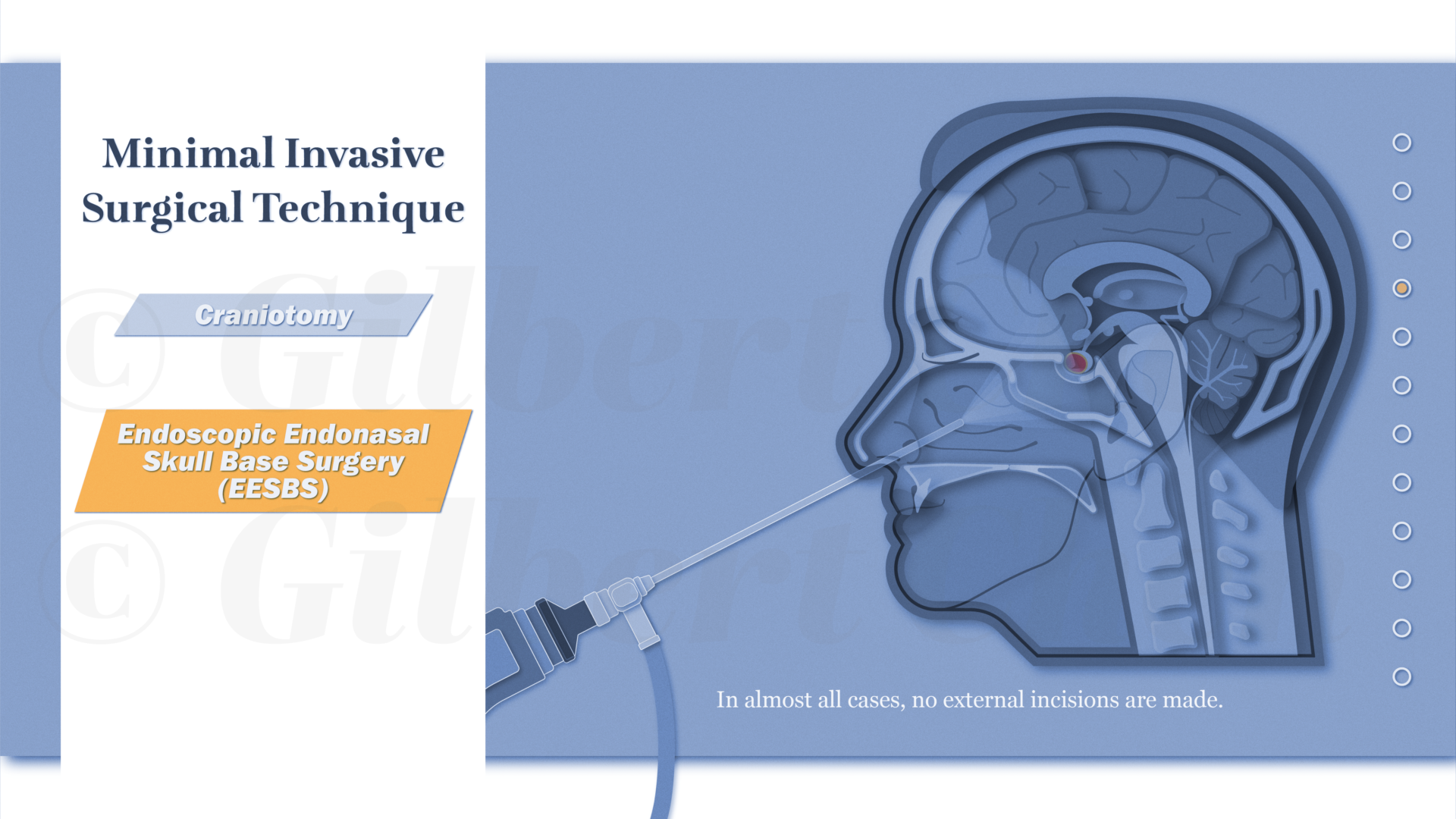
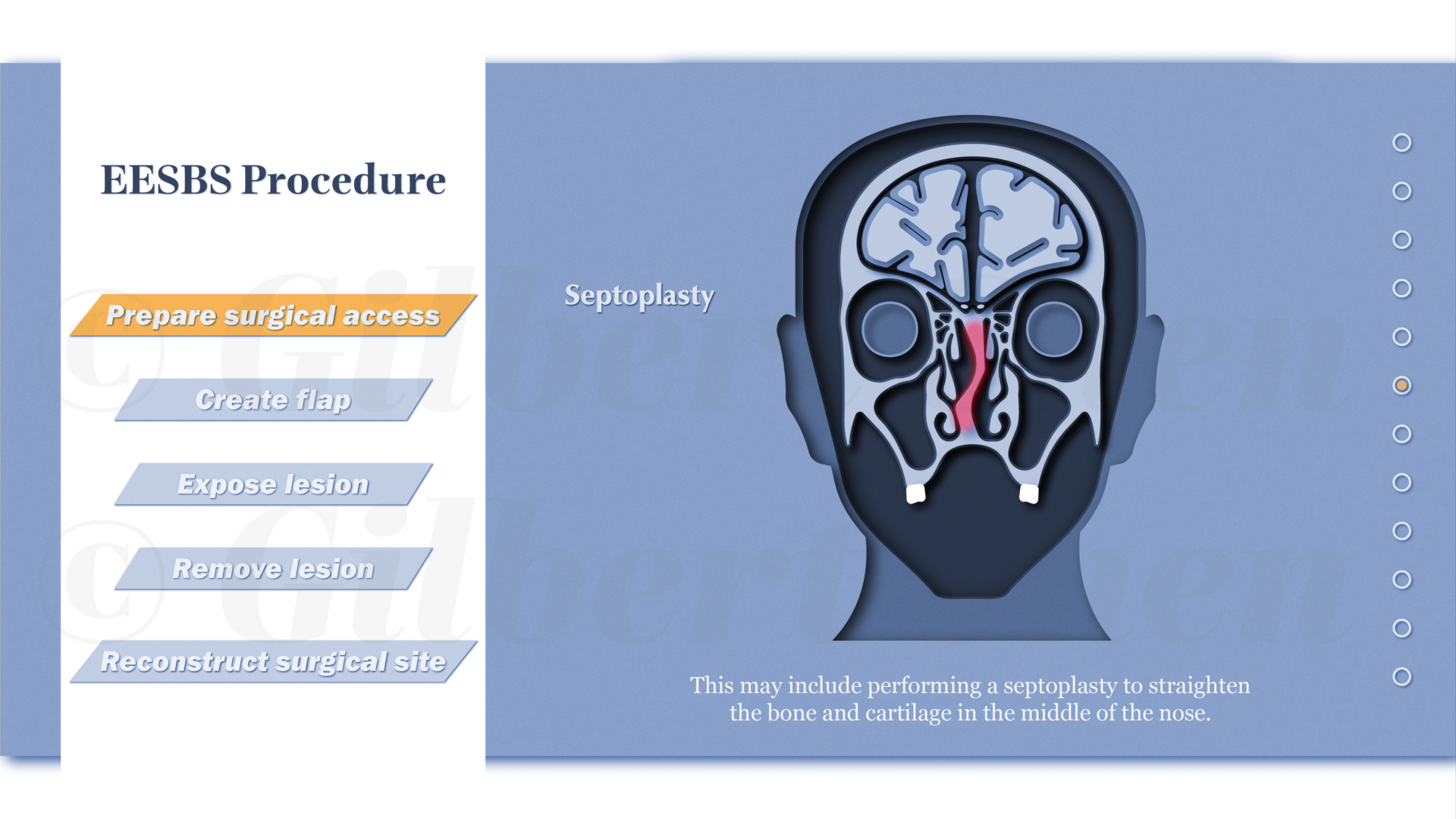
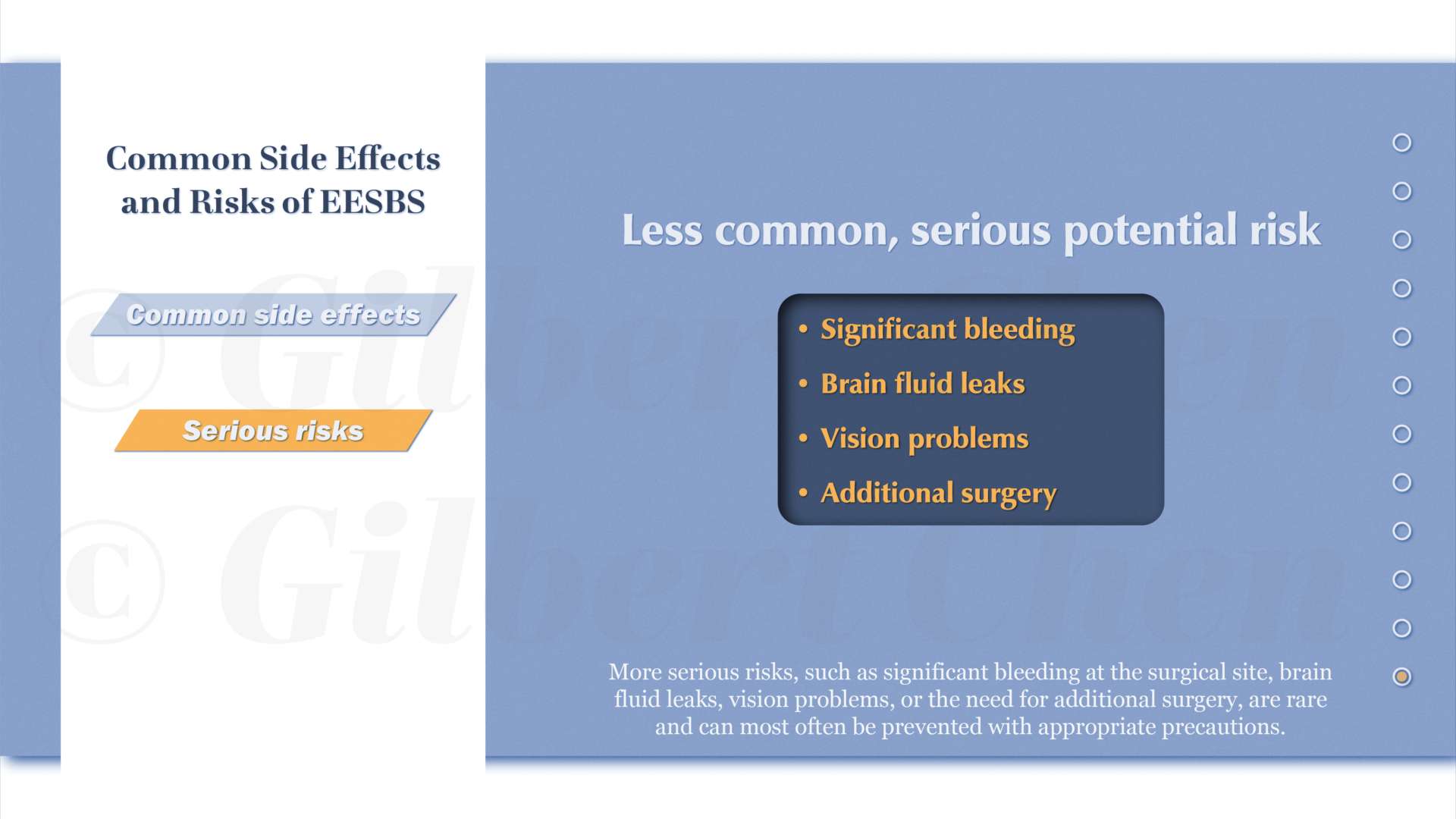
Endoscopic endonasal skull base surgery (EESBS) is a complex surgical approach used to access and remove pituitary lesions and tumors through the anatomically complex sinonasal corridor. Many patients find it difficult to understand and conceptualize the nuanced anatomy, surgical technique, and the substantial postoperative side effect and symptom profile associated with this minimally invasive surgical procedure.
Effective perioperative counseling is challenging in the setting of time-constrained preoperative visits and by the abstract surgical technique in an anatomical region that is unfamiliar to most patients. The goal of this project was to create an interactive and accessible resource available for both patients and surgeons alike to help improve perioperative counseling and patient education. This research involved using an Artificial Intelligence assisted workflow to create a series of 2D animations that aim to explain the treatment process using engaging, educational, and easy-to-understand content. Animations were designed to provide patients with an immersive experience to help explain relevant anatomy as well as preoperative, surgical, and postoperative treatment phases. The resulting narrated, 2D “cut paper” style animations are a resource to assist physicians with patient communication and education needs. Given its modular design, this resource can be edited or updated to reflect changes in surgical techniques and can be adapted into interactive e-learning materials.
Recognizing that generative Artificial Intelligence (AI) reached public awareness in early 2023 as a powerful tool for generating new content including text, images, and audio from existing online data, this project aimed to incorporate this novel technology to enhance patient education over traditional approaches. With the implementation of an AI-assisted creative workflow, we utilized 1) an AI art generator for style inspiration, 2) an AI chatbot for assistance in script drafting, and 3) an AI voice synthesizer for audio narration. The research also addresses some of the potential risks and concerns associated with applying AI-assisted tools to patient education content creation. By implementing these new technologies in the creative workflow, this research provides valuable insights into when and how to appropriately apply AI technology while creating patient education content. The use of AI-assisted technologies in creating patient educational resources represents an exciting new development in the field of medical communication.
Result – Story Board